The Robot
This page is under construction.
Introducing Your Robot
By default the robot will be a standard e-puck robot, which is a representation of a real robot. Alternatively teams may modify the standard robot in order to change the position or number of sensors and wheels.

Default Robot
If no custom robot design is loaded this default e-puck will be used.
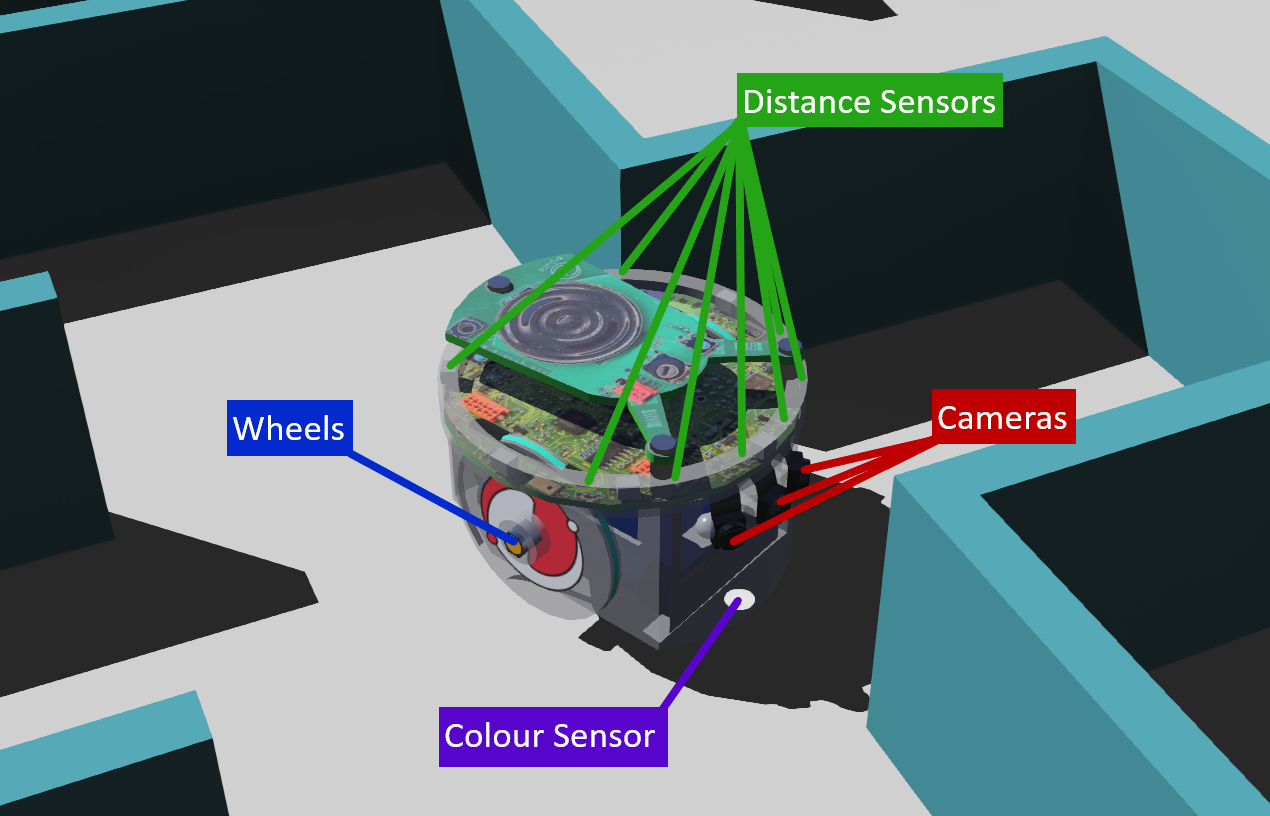
By default the e-puck robot has the following components:
- Wheels - One left and one right, with a motor each, controlled independently to control speed and turning.
- Distance Sensors - Eight distance sensors around the robot to detect walls and objects.
- Cameras - Three RGB cameras on the front of the robot to provide visual recognition and one camera pointing downwards to act as a colour sensor.
- Gyroscope - Which can be used to measure the rotational speed of the robot.
- Accelerometer - Which can be used to measure the acceleration (or change in speed) of the robot.
- GPS - Which can be used to get an absolute position value of the robot.
More information regarding this robot may be found here: https://github.com/cyberbotics/webots/blob/master/docs/guide/epuck.md
Custom Robots
Before the game begins a custom robot may be loaded from a .json file.
A tool to allow the teams to create these custom robots may be found here: https://v25.robot.erebus.rcj.cloud/
The basic structure of these robots will be the same but teams may customize the placement of different components as well as deciding which ones they want to use.
There is also a cost limit for the total parts of the robot, meaning that teams may be forced to prioritize certain aspects over others.
The components that may be added or adjusted are:
- Sensors
- Gyroscope - May be added and positioned
- GPS - May be added and positioned
- Cameras - Up to three may be added and positioned
- Colour Sensor - May be added and positioned
- Accelerometer - May be added and positioned
- Lidar Sensor - May be added and positioned
- Distance Sensors - Up to eight may be added and positioned
- Motors
- Wheels - Up to three may be added and positioned
Components
Motors
By default there are two motors, one connected to each wheel. Which are located on the left and right sides of the robot. The motors can be independantly conrolled in both speed and direction to allow for detailed movement control.
The robot may be customised to have between 1 and three motors and wheels and their placement can be changed as well.
They are simulations of stepper motors, with 20 steps per revolution with a 50:1 gear ratio.
Sensors
Here is a list of all the sensors available on the robot with a short description of their function.
Distance sensor
Infrared Sensors capable of gathering information regarding the distance to nearby objects directly in front of them. There are eight total sensors, six are spaced evenly around the front of the robot and two are spaced appart on the rear of the robot.
The number of distance sensors and their placement can be different when using a custom robot.
Colour sensor
The colour sensor is placed on the bottom side at the front of the robot. It allows the robot to gather information about the color of the floor below it.
Using a custom robot the position of this sensor may be changed.
Cameras
The three cameras are placed on the front of the robot, one straight ahead and the others angled to the left and right. These allow for visual recognition of the map and obstacles.
A custom robot may have fewer cameras and they may be placed differently.
Accelerometer
The accelerometer allows the robot to gather information about changes to its own velocity in the three axes.
LIDAR Sensor
The lidar sensor may be used to determine the distance between the position of the sensor and a solid object.
By default there is not a LIDAR sensor on the robot, one must be added with the customiser before it can be used.
Gyroscope
The gyroscope allow the robot to gather information about changes to its own rotation, regardless of its position.
GPS
The GPS sensor allows the robot to gather information about its current absolute position.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.